



Blog
Hot Category
Latest Blog
01 Jan 2025
Nlelsen
Globally, different countries and regions adopt varying standards for AC voltage, with 110V and 220V being the most common. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages, primarily in terms of safety, efficiency, and application scenarios.
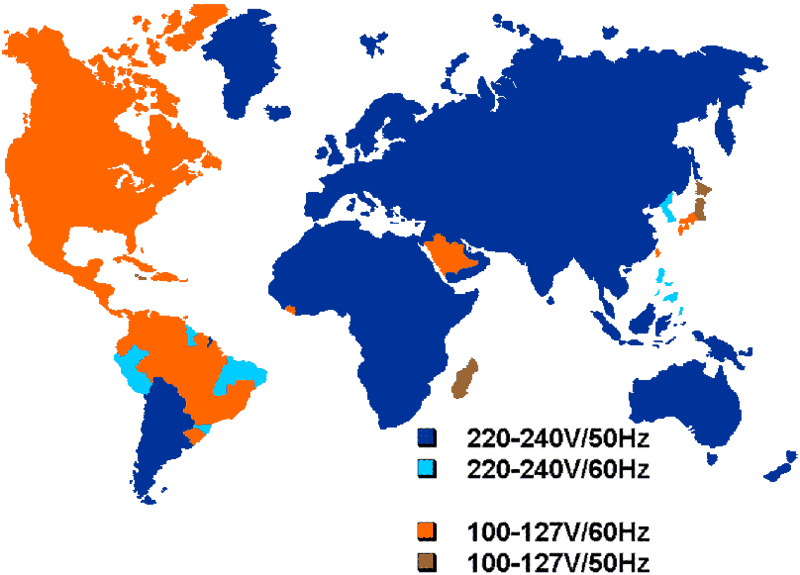
· Due to its lower voltage, 110V power systems pose less risk to human safety in case of electric shock, making them considered safer.
· Devices designed for 110V typically require lower insulation levels, which helps components withstand overloads or short circuits better, extending equipment lifespan.
· For home use, 110V appliances are highly compatible, especially for low-power devices like lighting and small household appliances.
· Compared to 220V systems, 110V requires higher current to deliver the same power, leading to increased energy loss in transmission and higher cable specifications.
· Due to the lower voltage, high-power devices such as air conditioners and heaters face operational limitations.
· The 220V system requires less current for the same power, resulting in lower energy loss and enabling power to be transmitted over longer distances.
· High-power equipment operates more efficiently on a 220V system, such as industrial appliances, motors, and heating equipment.
· Because of the lower current, smaller wire cross-sections are required, reducing wiring and installation costs.
· The higher voltage increases the risk of severe injuries during electric shocks, necessitating stricter safety measures.
· Higher voltage places more stress on device components, especially during startup and shutdown, potentially shortening equipment lifespan.
· Regional Factors: Countries like the United States and Japan predominantly use 110V, while Europe and China mainly adopt 220V, often for historical and economic reasons.
· Purpose:
For residential safety, 110V might be more suitable.
For industrial efficiency, 220V is the better choice.
· Device Compatibility: Voltage differences can affect appliance performance during international travel, necessitating the use of adapters or transformers.
Both 110V and 220V systems have their own merits and drawbacks, with distinctions in safety, efficiency, and applications. The choice between these standards depends on specific needs and environmental factors. Regardless of the voltage, ensuring the quality and safety of electrical equipment is paramount.