



Blog
Hot Category
Latest Blog
27 Aug 2024
Eli
As concerns about dwindling energy resources and sustainability continue to escalate, more and more people are applying solar panels as a viable alternative to traditional energy sources.But the question also arises: are solar backup batteries really worth the investment?
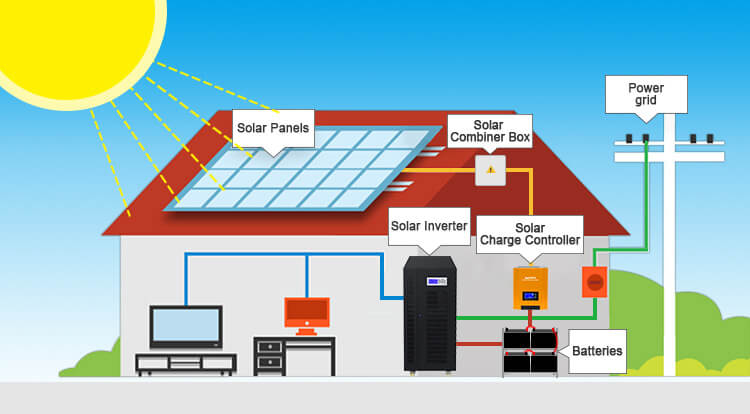
First of all, we have to understand what is a solar backup battery, in fact, photovoltaic system power generation does not need solar backup batteries, but if there is no solar backup battery, you must immediately use the generated solar energy. But solar power is typically generated during the day when the sun is shining, when electricity demand in most homes is lower.
Therefore, many families will input the electricity generated by solar power generation into the grid, and then buy it back at a high price when they need electricity, because the buyback price of the grid is relatively low, and the general ledger is calculated throughout the year, and the expenditure has not been significantly reduced.
With the solar backup battery, you usually produce more solar power will not have to input power into the grid but can be stored until you need electricity can be used directly, so that you can reduce a lot of electricity expenses.
① One of the most attractive benefits of installing solar energy is that they can save a home or business owner money on their electricity bills.
②Can reduce dependence on fossil fuels, national policies to promote the development of new energy.
③ In the power failure and emergency time can be uninterruptible power supply for electrical power supply.
④ Solar off-grid systems can also be in some remote areas not covered by the power grid, the system is completely off the grid for electrical power supply, which inevitably requires the use of solar backup batteries.

According to the current stage of social development, the popularity of solar backup batteries is inevitable, but the specific implementation needs to be determined according to the environment of each region and the size of space and economic conditions.
Solar Backup Batteries: Indispensable Energy "Reservoirs"
First, let's clarify a basic concept: photovoltaic systems themselves do not require backup batteries to generate electricity. Without batteries, the direct current produced by solar panels can be converted into alternating current by an inverter and used immediately by household appliances. However, the characteristics of solar energy—peak generation during the day when sunlight is abundant—significantly misalign with most households' peak electricity usage, which occurs in the evening and at night.
This creates a core contradiction:
Excess Daytime Electricity: When sunlight is abundant and electricity generation far exceeds immediate needs, the surplus energy, without battery storage, has no choice but to be fed back into the public grid (a process known as "net metering").
High-Cost Evening Electricity: In the evening and at night, household electricity demand surges, but solar power generation drops sharply or even to zero. Users have no choice but to purchase electricity from the grid at higher prices to meet their needs.
Economic Imbalance: The key issue is that the price at which grid companies buy back surplus electricity from users (feed-in tariff) is usually much lower than the price users pay to purchase electricity from the grid (retail electricity price). This "sell low, buy high" model greatly weakens the potential of solar systems to save on electricity bills. Even with annual settlements (net metering), the price difference means that the savings on electricity bills are often not as significant as expected.
Solar backup batteries are the key to solving this core contradiction. They play the role of a household energy "reservoir":
Capturing Excess Electricity: During peak daytime generation, they store surplus solar electricity that the household cannot use immediately, rather than selling it back to the grid at a low price.
Releasing Energy as Needed: After sunset, during peak usage hours, or when electricity prices are high, the stored electricity is released for direct household use.
Maximizing Self-Consumption: Significantly increasing the self-consumption rate of solar power, i.e., the proportion of solar power directly used by the household, thereby maximizing the reduction in the need to purchase high-priced electricity and substantially lowering electricity expenses.
Multidimensional Advantages of Investing in Solar Backup Batteries
The benefits of installing solar backup batteries go far beyond saving on electricity bills; it is a win-win investment:
Significant Economic Benefits: Sharp Reduction in Electricity Bills
Core Value: This is the most direct and appealing advantage. By significantly increasing the proportion of solar power used directly, avoiding peak grid electricity prices, household electricity bills will show a notable decrease. For regions with high electricity prices and large peak-valley price differences, the payback period for the investment is shorter.
Hedging Against Rising Electricity Prices: Locking in part of the energy costs reduces the uncertainty risk brought by future continuous electricity price increases.
Energy Independence and Resilience: A Bulwark Against Power Outages
Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS): In the event of unexpected grid interruptions (such as extreme weather or equipment failures), the backup battery system (usually paired with specific inverters) can seamlessly switch to provide continuous power for critical loads (refrigerators, lighting, communication equipment, medical devices, etc.), ensuring basic household living needs and safety. This is especially important in disaster-prone areas or regions with unstable grids.
Off-Grid/Microgrid Operation Foundation: For remote areas without grid coverage, solar backup batteries are a core component for building completely independent solar off-grid systems, providing stable power for entire residences or facilities.
Environmental Contributions: Driving Green Transformation
Maximizing Clean Energy Utilization: Battery storage increases the actual utilization rate of solar energy, allowing more green electricity that would otherwise be wasted or sold back to the grid at low prices to be truly consumed locally.
Reducing Fossil Energy Dependence: By reducing the need to purchase electricity from the grid (usually supported by fossil energy generation) during peak periods, it indirectly lowers overall carbon emissions and dependence on fossil fuels, positively responding to global and national policies promoting new energy development (such as China's "dual carbon" goals).
Optimizing Grid Operation: Potential Auxiliary Services
Peak Shaving and Valley Filling: Large-scale household storage systems discharge during peak periods and charge during off-peak periods, objectively helping the grid balance loads, reduce peak-valley differences, and improve grid operation efficiency and stability.
Future Potential (VPP): With the development of virtual power plant (VPP) technology, dispersed household storage systems may be aggregated in the future to participate in grid frequency regulation, demand response, and other auxiliary services, potentially providing users with additional benefits.